
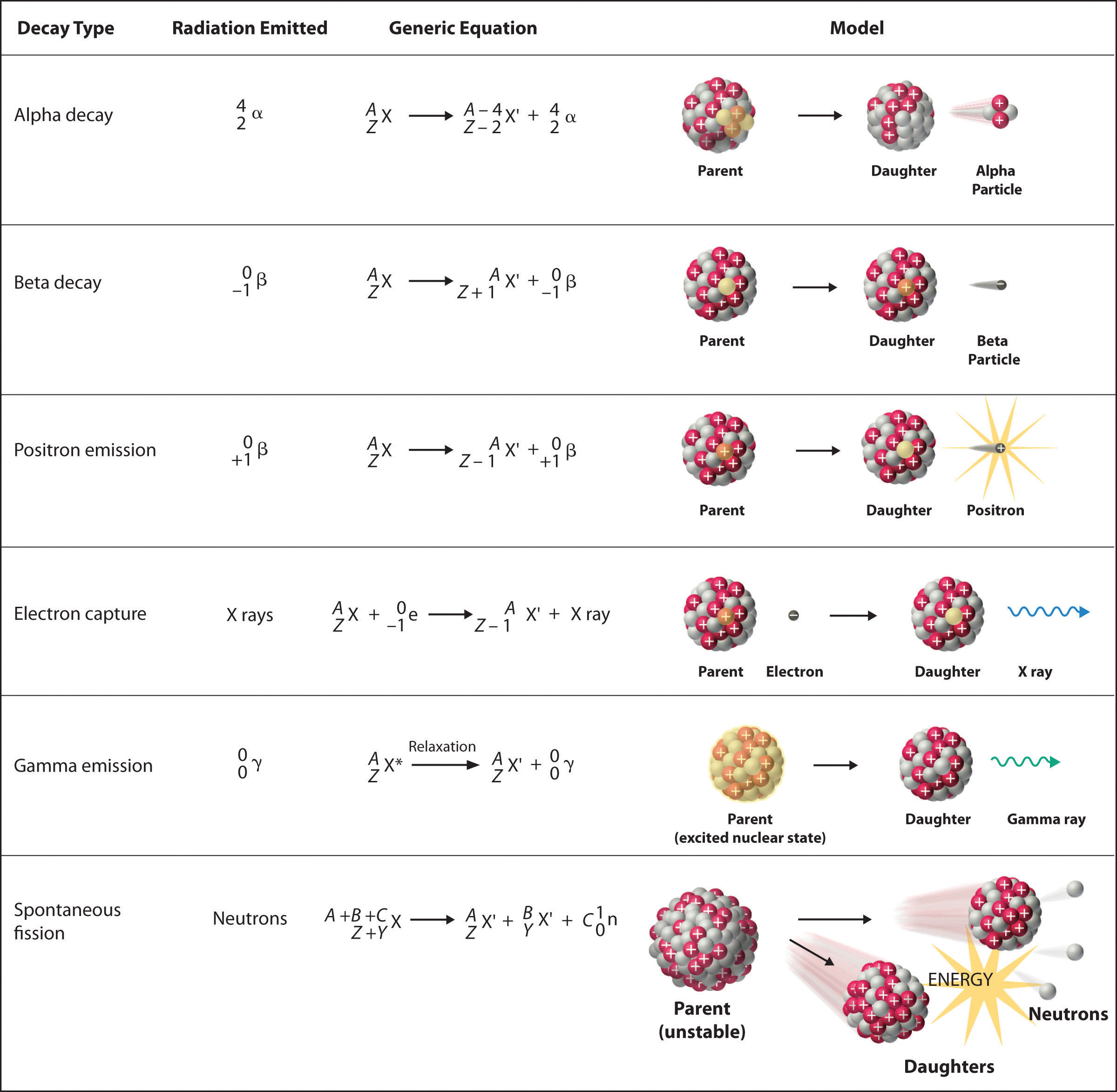
The products formed will also undergo spontaneous disintegration, releasing further particles and energy. In some cases, the reaction may produce smaller products, such as radiation and neutrons, as well as alpha particles or tritium. However, it is estimated that the products will split into almost equal masses, resulting in heavy elements and radioactive particles. The products released during the fission process vary depending on the reaction, with different velocities and energies. On average, uranium-235 produces 83 terajoules per kilogram after fission, which is equivalent to 23.05 gigawatt-hours per kilogram of fissile material. In nuclear reactors, the residual energy is heat, which is used to create high temperatures and pressurized steam. These photons and products slow down and convert into residual energy, which is used to produce work. The energy released during the induced fission processĭuring fission, energy is released in two forms: kinetic energy given to the neutrons and products, and high-energy photons (gamma rays). The neutron has to pass close to the nucleus and be attracted to it by the strong nuclear force to be absorbed by the nucleus. Slow neutrons are used because they are more likely to be captured by heavy nuclei. Fast-moving neutrons collide with the atoms of water or graphite and transfer some of their energy to them. In many nuclear reactions, fission is present in water or graphite. Slow neutrons are necessary for this process.
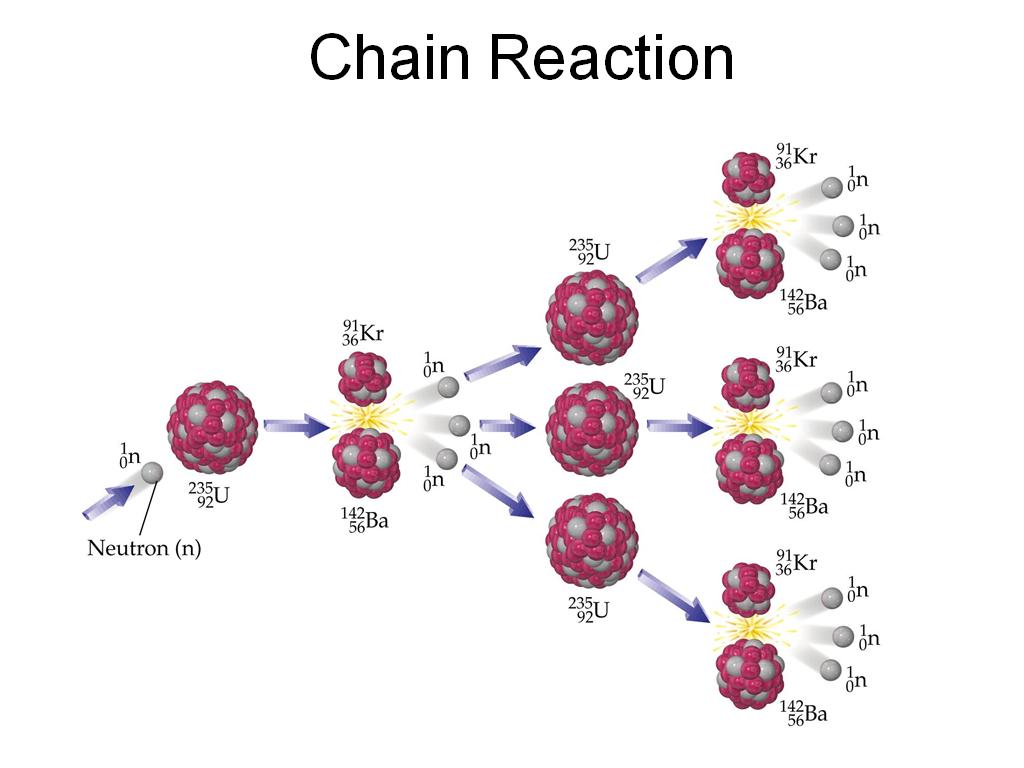
It works by slowing down fast-moving neutrons so they can be captured by heavy nuclei. A moderator is used to reduce this energy. It reaches an average of 200 terajoules per kilogram, which is equivalent to 6.6% of the speed of light in a vacuum. The energy released during fission is huge. The chain reaction of uranium-236 when produces products and neutrons The neutrons are captured other uranium-235 atoms, turning into-236 This process repeats as the new isotopes are unstable.
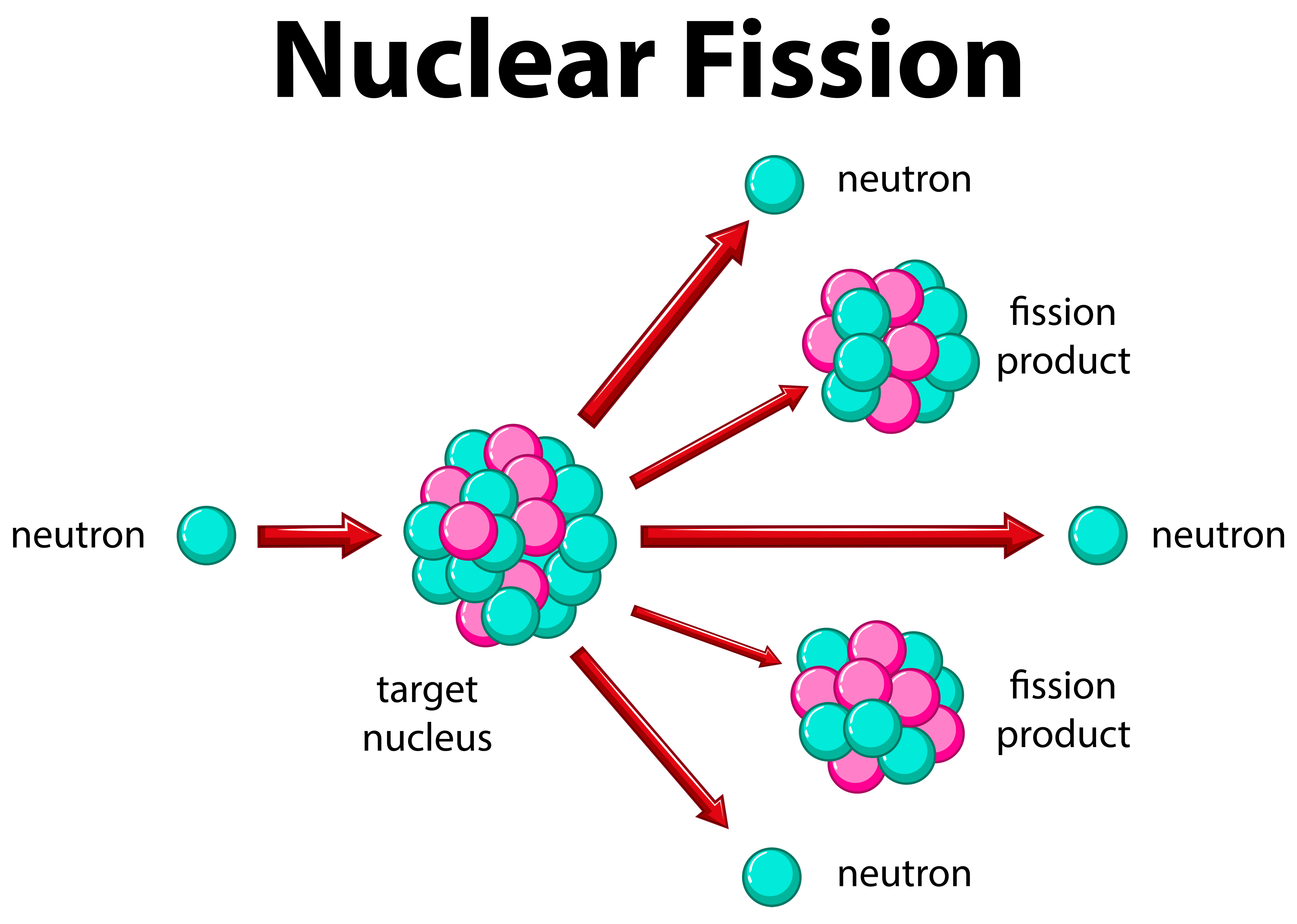
When uranium-235 accepts another neutron, it turns into uranium-236. The slowed-down neutrons can start another fission reaction in another fissile atom. The reaction produces two or three neutrons that move very fast. Neutron-induced fissionĭuring induced fission, neutrons make heavy nuclei unstable. The reaction also releases other neutrons and high-energy photons. When the heavy elements break apart, they create two lighter elements called fission products. Scientists shoot slow-moving neutrons at heavy radioactive materials like uranium-235 or plutonium-239. Induced fission is like a "forced decay".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
